How to Eat Whole Food Plant-Based Diet in South Africa?

Introduction
Eating a whole food plant-based diet in South Africa is unlike any other diet you experienced.
If you read no more than one message about health and nutrition this year, this health topic should be it.
Did you know?
There are many places in the world where people live longer. Where achieving age levels exceeding one hundred healthy years in common.
What is their secret?
The key has been the plant-based diets. Among these plant-based diets, the whole food plant-based diet stands out as a powerful and transformative approach to nourishing our bodies.
But here is a kicker:
The man considered the father of medicine by health professionals everywhere is Hippocrates. This famed Greek physician made a vital discovery over two thousand years ago.
There is a clear connection between nutrition and health.
Where is this all going?
This post will explain how to eat a whole food plant-based diet. Looking at health benefits of a whole food plant-based diet.
Tips for transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle. We will also delve into building a nutrient-dense meal plan for optimal health.
This post is your go-to comprehensive guide on how to eat a whole food plant-based diet in South Africa.
Now:
What is a whole food plant-based diet?
Chapter One
What is a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet (WFPB)
A whole food plant-based diet emphasizes consuming natural, unprocessed foods derived from fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Whole food plant-based (WFPB) excludes animal products and highly processed foods.
So, the underlying principle of a whole food plant-based diet is two-fold:
Whole foods that are natural without processing. Eating foods that are not heavily refined and processed.
Also, eat foods that come from plants – plant-based. Excluding animal products and ingredients such as milk, eggs, meat, and honey.
It gets better:
Whole food is plant-based and is not a diet of vegetables only.
You do not rely on counting calories and worrying about nutrients.
You eat a variety of foods. Foods such as:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Tubers
- Whole grains
- Legumes
Is eating a whole food plant-based diet (WFPB) like vegan or plant-based?
The critical factor in a whole food plant-based diet is the elimination of oils.
The folks from Fork Over Knives have illustrated this difference clearly.
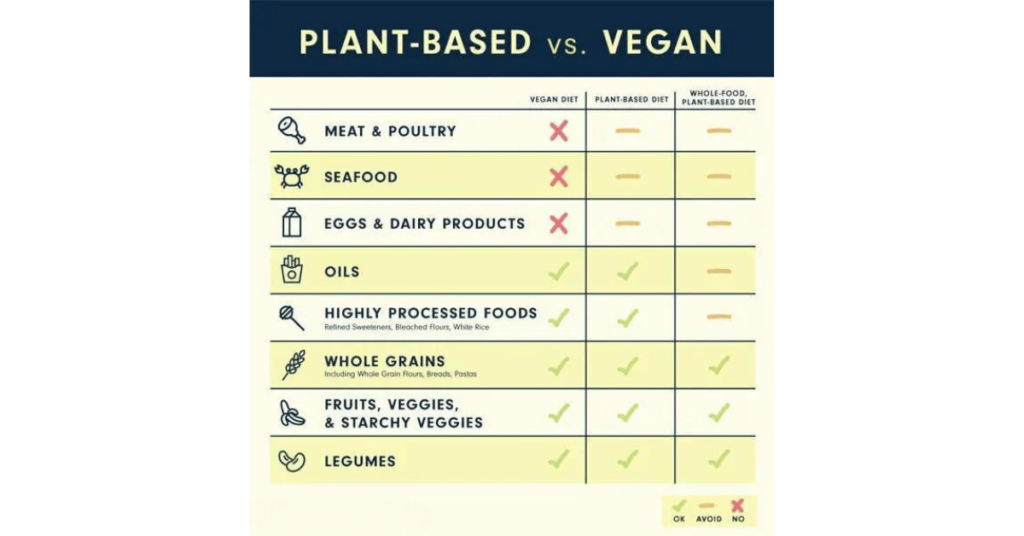
Source: Forks Over Knives
This dietary choice benefits our health and has positive implications for the environment.
Chapter two gives you the fundamental principles of a whole food plant-based diet.
Chapter Two
The Key Principles of a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet
Adopting a whole food plant-based diet is not just a passing trend.
This lifestyle choice has gained recognition for its many health benefits.
Did you know that shifting your focus to eating whole foods that are plant-based will significantly improve your well-being?
Yes!
Just eat more fruits and vegetables and incorporate whole grains and legumes. Also, reduce processed foods and animal products.
Eating More Fruits and Vegetables
The first fundamental principle of a whole food plant-based diet is increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetables.
These natural powerhouses contain essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote optimal health.
Do you want to ensure your body receives the nutrients for vitality and disease prevention?
Incorporate a variety of colourful produce into your meals.
Focusing on Whole Grains and Legumes
Another essential principle is to prioritize whole grains and legumes.
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide complex fibre-rich carbohydrates. The fibre helps to regulate blood sugar levels and maintain digestive health.
Legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent protein sources while low in saturated fat. They also contain fibre, which aids in digestion and promotes satiety.
Reducing Processed Foods and Animal Products
Reducing processed foods and animal products is another crucial aspect of this dietary approach.
Processed foods often contain elevated added sugars, unhealthy fats, sodium, preservatives, and artificial additives. These processed foods can have detrimental effects on your health. Minimizing or eliminating your consumption from your diet will reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Similarly, reducing animal products like meat and dairy helps decrease the intake of saturated fats and cholesterol. At the same time, increasing the intake of plant-based proteins and healthy fats in sources like nuts, seeds, and avocados.
Eating a whole food plant-based diet in South Africa based on these critical principles offers many benefits. Benefits include improved heart health and better weight management. WFPB enhances digestion and reduces inflammation.
Opting for WFPB lowers risk factors for chronic diseases.
Let us unpack these health benefits of a whole food plant-based diet.
Chapter Three
The Health Benefits of a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet
What is so special about eating a whole food plant-based diet in South Africa? What makes it the best option among other diets?
Improved Heart Health
One of the benefits of a plant-based diet is its impact on heart health.
Research shows that plant-based diets reduce blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
The abundance of fibre, vitamins, and minerals in whole plant foods helps to support optimal heart function.
Whole Food Plant-Based Diet and Weight Management
Weight management is another advantage of embracing a whole food plant-based diet.
Plant-based foods have low caloric content and are fibre-rich than animal products.
This combination promotes satiety. Low-caloric content and fibre help you maintain a healthy weight or shed excess pounds.
Moreover, the high nutrient density of plant-based foods ensures that you receive essential nutrients while controlling your calorie intake.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Disease

Furthermore, a whole food plant-based diet helps reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases.
It also helps in inflammatory conditions. The phytonutrients in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains possess potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties supporting health and well-being.
Eating a whole food plant-based diet can pave the way towards better long-term health outcomes.
By exploring these topics thoroughly,
we aim to provide valuable insights into why incorporating more plant-based foods into your daily meals gives you a more sustainable lifestyle.
Lowering Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Naturally
Lowering cholesterol and blood pressure is a goal shared by many individuals looking to improve their well-being.
Several strategies and lifestyle changes can help achieve this. Strategies include incorporating cholesterol-lowering foods and a plant-based diet for high blood pressure.
Modify your diet and give your body the most effective ways to lower cholesterol levels. Consuming foods rich in soluble fibre, such as oats, legumes, and fruits, can help reduce LDL (harmful) cholesterol levels.
Additionally, incorporating heart-healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and seeds can positively impact cholesterol levels.
Plant-based diets are low in sodium and high in potassium-rich foods like leafy greens, bananas, and sweet potatoes. This combination helps promote healthy blood pressure levels by reducing sodium intake while increasing potassium intake.
Embracing these strategies provides an opportunity for long-term health benefits that go beyond just numbers on a chart.
Boosting Immunity and Preventing Illness
Plant-based immune system support is popular because it boasts vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
These nutrients are vital in strengthening the body’s defences against illnesses and diseases. Adding a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds will provide you with the essential nutrients needed for optimal immune health.
Whole foods offer a natural and sustainable approach to boosting immunity.
Unlike synthetic supplements or processed foods that may contain artificial additives or preservatives, whole foods provide pure nutrition straight from nature.
By consuming a diverse range of colourful fruits and vegetables, you can benefit from their unique array of phytochemicals shown to enhance immune function.
By nourishing your body with nature’s bounty of nutrients and antioxidants, you can fortify your defences against common ailments while enjoying the many benefits of a wholesome diet.
You have explored the whole food plant-based diet principles and its health benefits.
Here are the steps you will take to achieve these health outcomes.
Chapter Four
Step 1: Tips for Transitioning to a Whole Food Plant-Based Lifestyle
Transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle can be transformative and rewarding.
By making gradual dietary changes, you can effectively embrace this lifestyle without feeling overwhelmed. Here are some valuable tips to help you ease into this new way of eating and discover delicious plant-based recipes.
- Take it one step at a time. Add more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to your meals. Then, gradually reduce your intake of animal products. Thus making the transition more sustainable.
- Explore many plant-based ingredients available to you. Experiment with different fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds. Eating extra fruits will add variety and excitement to your meals. Don’t be afraid to try new flavours and textures.
- Seek inspiration from reliable sources such as cookbooks, online recipe platforms, or cooking classes tailored explicitly to plant-based diets. These resources offer a wealth of delicious recipes to keep you motivated.
Remember that transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle in South Africa doesn’t mean sacrificing taste or enjoyment in your meals. It opens kitchen creativity opportunities as you explore new flavours and combinations.
Embrace this adventure with an open mind and allow yourself to savour the incredible tastes that nature has provided us with.
By following these tips and embracing the abundance of delicious plant-based recipes available, transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle can become an enjoyable process of health benefits for both body and mind.
Step 2: Busting Common Myths About the Whole Food Plant-Based Diet
Do you need clarification about the diets out there?
When talking to your friends and colleagues, they discredit your new lifestyle for lack of proteins and other nutrients!
One of the most prevalent misconceptions is protein intake in plant-based diets. Many believe it is challenging to obtain sufficient protein from solely plant sources.
However, this couldn’t be further from the truth.
Legumes, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and nuts must be part of your meals. They can quickly meet the recommended daily intake.
Research shows that most individuals on a whole food plant-based diet consume adequate protein without additional supplementation.
Furthermore, these plant-based proteins often have added benefits such as fibre and essential nutrients unavailable in animal-based proteins.
It’s important to note that a well-balanced whole food plant-based diet can provide all the necessary amino acids for optimal health. You can fulfil your protein needs by incorporating various plant foods into your meals while enjoying multiple flavours and textures.
So, let’s bust this myth once and for all.
You don’t need to worry about inadequate protein intake on a whole food plant-based diet. With proper meal planning and knowledge about nutrient-rich plant sources, you can thrive nutritionally and ethically on this dietary choice.
Step 3: Overcome Common Challenges and Maintain a Whole Food Plant-Based Lifestyle
Transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle can face its fair share of obstacles.
But good strategies can overcome these obstacles, allowing you to maintain a healthy and sustainable plant-based diet.
One of the most common challenges individuals face in adopting a plant-based lifestyle is socializing.
It can be inaccessible when attending gatherings or dining out with friends and family who may not follow the same dietary choices.
But fear not; there are effective ways to navigate these situations while staying true to your plant-based principles.
Here is what you can do:
- Communicate your dietary preferences politely but assertively. Letting others know about your nutritional choices will help them make accommodations or provide alternative options. They can also offer to bring a dish or suggest restaurants with plant-based menu options. These offers can make socializing more accessible for both you and your companions.
- The challenge of finding suitable alternatives for favourite non-plant-based foods. Fortunately, there are numerous delicious and nutritious plant-based substitutes available today.
- Experimenting with different types of recipes and exploring new ingredients can help you recreate familiar flavours while still adhering to your whole food plant-based diet. Maintain motivation during challenging times. Surround yourself with people who share similar dietary goals. They can provide support and encouragement along the way. Joining online communities or local groups focused on whole food plant-based eating can offer valuable advice, recipe ideas, and even opportunities for group meet-ups or potluck gatherings.
Step 3: Building a Nutrient-Dense Meal Plan for Optimal Health
Creating a nutrient-dense meal plan is essential for optimal health, especially for plant-based diets.
By carefully selecting and combining various food groups, you can give your body all the necessary nutrients to thrive.
A nourishing meal plan should provide balanced nutrition, incorporating various plant-based protein sources, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Balanced nutrition ensures you meet your daily caloric needs and fuel your body with the essential building blocks.
When building your meal plan, consider including protein-rich foods such as legumes (beans, lentils), tofu, tempeh, and quinoa.
These protein sources in plant-based foods provide all the vital amino acids needed for proper bodily functions. Adding whole grains like brown rice or oats will provide complex carbohydrates for sustained daily energy.
Remember to include abundant fruits and vegetables in your meal plan, as they are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for various colours to ensure you get a wide range of nutrients.
To round out your nutrient-dense meal plan, incorporate healthy fats. Healthy fats like nuts and avocados are critical for brain health and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
STEP 4: Incorporate Variety into Your Whole Food Plant-Based Meals
You can enjoy delicious plant-based breakfast, lunch, or dinner meals with the right recipe ideas.
With breakfast, there are plenty of tasty options to kickstart your day.
How about trying a hearty tofu scramble loaded with colourful vegetables and spices? Or a stack of fluffy vegan pancakes topped with fresh fruits and maple syrup?
These recipes will meet your needs and provide essential nutrients to fuel your day.
You can explore a world of flavours for lunch by experimenting with different grains, legumes, and vegetables.
A nourishing Buddha bowl filled with quinoa, roasted sweet potatoes, avocado slices, and a tangy tahini dressing can be satisfying and visually appealing.
Alternatively, you can try a vibrant chickpea salad wrap packed with crunchy veggies and zesty dressing for a refreshing midday meal.
Dinner is the perfect time to get creative in the kitchen.
How about indulging in mouthwatering plant-based burgers made from black beans or lentils? Serve them on whole grain buns alongside oven-baked sweet potato fries for a guilt-free treat.
Are you looking for something lighter yet equally flavourful?
Consider making a colourful stir-fry with various vegetables and protein-rich tofu or tempeh.
Incorporate variety into your whole food plant-based meals throughout the day. You can ensure you get various nutrients while satisfying your taste buds.
So don’t hesitate to explore new recipes and experiment with different flavours – endless possibilities!
Conclusion
Now that you know how to eat a whole food plant-based diet in South Africa and that it is a surefire way of gaining optimal health and well-being.
All that is left is for you to do what it takes to live a healthy life.
To do that, you need to get leverage on yourself.
A whole food plant-based diet can succeed when implemented precisely as prescribed.
But diet or lifestyle programs, no matter how powerful, will only work if there is the power of commitment behind it.
Now I would like to hear from you.
What steps are you taking?
Are you going to incorporate more whole food plant-based in your meals? Or are you taking one tip for transitioning to a whole food plant-based lifestyle?
Either way, let me know by leaving a comment below right now.
